When planning an algorithm, diving straight into code can be overwhelming. That’s where pseudocode comes in — a simple, language-agnostic way to outline your logic without worrying about syntax. Think of it as fake code used for brainstorming, structuring ideas, and communicating algorithms clearly before you start coding.
DATA TYPES IN PROGRAMMING:
- STRING => Text, anything within strings (“12345”)
- INTEGER => numbers that are not in strings
- BOOLEAN=> either true or false
- CHAR=> a single character
- REAL=> decimal point values
Syntax That Needs To Be Remembered!
- OUTPUT => used to output any value
- INPUT => used to take any input from the user
3 TYPES OF LOOPS
Why do we even loops? Loop is a piece of code that repeats a number of times so that we dont have to write the same code multiple times. For more info on loops go over the topic: What even is a loop? We have 3 types of loops in pseudocode:
- FOR LOOP => COUNT CONTROLLED LOOP
- WHILE-DO-ENDWHILE LOOP = PRE CONDITION LOOP
- REPEAT UNTIL LOOP =POST CONDITION LOOP
- for loop is mainly used when we know the number of times we want to loop through a set number of statements.
- while and repeat until are mainly used when we don’t know the number of times we want to loop through a set of statements
Code Examples Of Loops:
For Loop:
FOR index <- 1 TO 50
OUTPUT "*"
NEXT index
While Loop
index = 1
while index<=5 DO
OUTPUT "*"
index = index +1
ENDWHILE
Repeat Until Loop
REPEAT
index = 1
OUTPUT"*"
index = index +1
UNTIL index <=5
Practice Questions:
Take a number as input and print the number of stars desired by the user.
STRING stars
OUTPUT "Enter a number"
INPUT stars
FOR index <- 1 TO stars
OUTPUT "*"
NEXT index
Q) Lets assume that we are making a program for a restaurant. The restaurant takes orders throughout the day and eventually closes the day by typing 0 as the order value. Create a program that takes the total order value and outputs it at the end of the day.
INTEGER Total, orderVal
Total,count = 0
REPEAT
OUTPUT "Enter the order value"
INPUT orderVal
count = count+1
Total = Total + orderVal
UNTIL orderVal =0
OUTPUT "The total order value throughout the day was ", Total
OUTPUT "The average order value was ", Total/count
1D Arrays
Declaring a 1D array:
DECLARE studentNames: ARRAY [0: 49] OF STRING
Assigning Values to the Array:
studentNames[0] = "Ali"
studentNames[1] = "Abdullah"
// Taking input from user to store the name at the user defined position
OUTPUT "Enter the name of the student: "
INPUT studentName
OUTPUT "Enter the position: "
INPUT position
studentNames[position] = studentName
Practice Questions:
Q) Take input of names of 10 students from the user and store them in an array.
DECLARE StudentNames: ARRAY[1:10] OF STRING
FOR index 1 TO10
OUTPUT "Enter name of student"
INPUT studentName
StudentNames[index] = studentName
NEXT index
Q) Take input from user of the number of students and store names of those many students in the array.
DECLARE number: INTEGER
OUTPUT "Enter number of students"
INPUT number
DECLARE Names: ARRAY [1:number] OF STRING
FOR index 1 TO number
OUTPUT "Enter the name of the student"
INPUT name
Names[index] = name
ENDFOR
Take input of marks of 10 students from the user and store them in an array. Then find the average of these marks.
DECLARE sum: INTEGER
DECLARE average: REAL
sum = 0
DECALRE Marks: ARRAY[1:10]
FOR index 1 TO 10
OUTPUT "Enter Marks: "
INPUT StudentMarks
sum = sum + StudentMarks
Marks[index] <= StudentMarks
NEXT index
average = sum/10
EFFICIENT CODE FOR LINEAR SEARCH:
Linear Search is a program that is used to find an element in the array. Below is an efficient implementation of it:
Q) Assume that we have an array StudentNames that has 100 names in it. (StudentNames[100]). Write code to take the name input from user and output the corresponding position of where the name is stored in the array.
DECLARE Value: STRING
DECLARE index INTEGER
DECLARE Found BOOLEAN
Found = False
index = 0
OUTPUT "Enter a name to be found in the array: "
INPUT value
REPEAT
IF value = StudentNames[index] THEN
Found = TRUE
ELSE
index = index +1
ENDIF
UNTIL Found = TRUE OR index >100
IF Found = TRUE THEN
OUTPUT "The value was found at ", index
ELSE
OUTPUT "The value was not found"
Random Practice Question:
Assume that we have an array StudentMarks[200]. Find the number of student who scored the marks that the user entered.
DECLARE Marks, sum,highest,lowest, total : INTEGER
total =0
lowest= 999
highest = -1
sum =0
OUTPUT "Enter a number"
INPUT Marks
FOR count 1 TO 200
IF studentMarks[count] > Marks THEN
sum = sum +1
ENDIF
IF highest < StudentMarks[count] THEN
highest = StudentMarks[count]
ENDIF
IF lowest > StudentMarks[count] THEN
lowest = StudentMarks[count]
ENDIF
total = total + studentMarks[count]
ENDFOR
average = total/200
OUTPUT "The number of students with", Marks "marks", "are ", sum
OUTPUT "The highest marks are", highest
OUTPUT "The lowest marks are", lowest
OUTPUT "The average marks of the students are", total/200
Efficient Bubble Sort Code For 1D Array
Bubble sort is a type of sorting that sorts the arrays in either ascending or descending order. In the example below, we assume that we already have an array named Scores[1:10] (10 elements) with integer values stored in it. It is efficient because if the array provided is already sorted, it doesnt keep on running the program.
count = 1
upperbound = 10
REPEAT
upperbound <= upperbound -1
swap <= FALSE
FOR index <- 1 to upperbound
IF Scores[index] > Scores[index+1]
temp <-- Scores[index]
Scores[index] = Scores[index + 1]
Scores[index+1] = temp
swap = TRUE
ENDIF
NEXT index
count <= count + 1
UNTIL index>9 OR swap = FALSE
2D ARRAYS
Declaring a 2D ARRAY:
DECLARE StudentMarks: ARRAY [1:100,1:2] OF INTEGER
Declares(creates) a 2D array named Student Marks with 100 rows and 2 columns that accept integer values.
Assign Values to the 2D array:
StudentMarks[1,1] <= "Abdul Rehman"
StudentMarks[1,2] <= "80"
Stores “Abdul Rehman” in the first row and first column and “80” in the first row, second column.
Practice Questions
Q) Assign values to all positions in the array by taking input from the user.
DECLARE Names: STRING
DECLARE ID: STRING
DECLARE StudentNames[1:1000,1:2] AS STRING
FOR count 1 TO 1000
OUTPUT "Enter name of the student"
INPUT Names
OUTPUT "Enter ID of the student"
INPUT ID
StudentNames[count][1] <= Names
StudentNames[count][2] <= ID
NEXT count
Q) Write code that takes ID as input and outputs the corresponding name to that ID.
DECLARE ID: STRING
DECLARE FLAG: BOOLEAN
Flag = FALSE
OUTPUT "Enter your desired ID"
INPUT ID
FOR index 1 TO 1000
IF ID = StudentNames[index][2]
OUTPUT StudentNames[index][1]
Flag = TRUE
ENDIF
NEXT index
IF Flag = FALSE THEN
OUTPUT "The value was not found"
ENDIF
Functions and Procedures
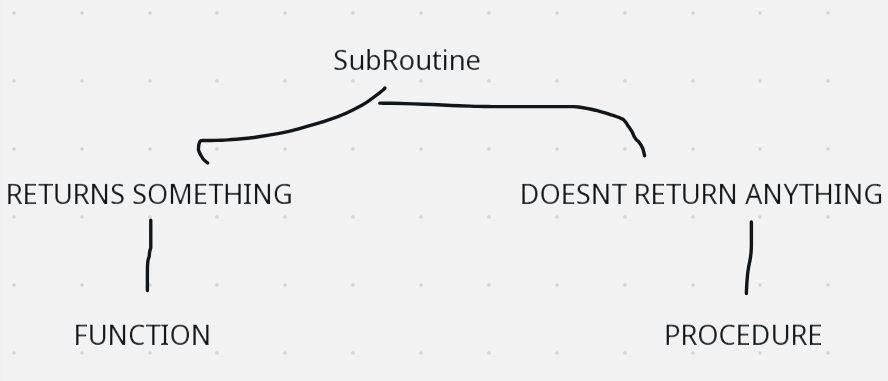
Creating A FUNCTION:
FUNCTION CalculateAverage(Sum: INTEGER, Total:INTEGER) RETURN REAL
Average = Sum/Total
RETURN Average
ENDFUNCTION
Creates a Function CalculateAverage() that will return a REAL value and that needs 2 parameters; Sum and Total.
Calling/Using the Function:
Avg1= CALL CalculateAverage(687,9)
Avg2 = CALL CalculateAverage(724,8)
Calculates the average and stores it in the corresponding varaibles.
Declaring/Creating a Procedure:
PROCEDURE PrintStars(NumOfStars:INTEGER)
FOR index 1 TO NumOfStars
OUTPUT "*"
NEXT index
ENDPROCEDURE
Creates a Procedure PrintStars() that will print the number of stars the user will demand(value passed in the parameter).
Calling a PROCEDURE:
CALL PrintStars(8)
OUTPUT SCREEN:
"********"
